flow cytometry results for lymphoma
Flow cytometry plays an important role in the diagnosis monitoring and treatment of haematological malignancies. Its also used to diagnose and classify leukemia or lymphoma.

B Flow Cytometry On Peripheral Blood Revealed An Abnormal Population Download Scientific Diagram
4 immunohistochemistry is sub-optimal for multiple antibody labelling or quantification of antigen expression and may be difficult to interpret due to.
. SPF are very high 30 as is the proliferation marker Ki-67 100 Example Dot Plots. A broad range of immunophenotype patterns are interpreted for various type of leukaemia lymphoma. RESULTS A diagnosis of lymphoma with subtyping was obtained in 88 of all cases in 85.
Therefore flow cytometry is an important integral part of lymphoma diagnosis even in cases where it cannot give a definitive diagnosis. CASE -1 Case 1 showed several immunophenotypic deviations in addition to lack of SIg light chain expression. Flow Cytometry Leukemia and lymphoma analysis by flow cytometry aids in identifying the tumor lineage which in most cases is identified as T cell B cell or myeloid.
Test Code Specialty Hematopathology Synonyms. Not always strictly speaking not very often. Tumor cells are positive for CD45 the B cell markers CD19 CD22 and CD79a with a monoclonal light chain expression of kappa or lambda.
Briefly the cells are individually passed in front of a laser where they are further sorted and characterized. Flow cytometry is generally used as follow up testing after a complete blood count CBC or white blood cells scan WBC. These cells were in the subsequent anlysis.
These may be the first indication of a possible blood cell cancer. The blast markers CD34 and TdT are negative. DISCUSSION The clinical significance of FCM for the detection of LMD has been evaluated in several studies thus far.
Overall survival in cases with diffuse large B cell lymphoma according to the results of flow cytometry FCM. The goal of the survey which was sponsored by the Clinical Cytometry Society CCS was to document what directors of flow cytometry laboratories currently consider to be the appropriate contents of a clinical leukemialymphoma phenotyping analysis and in what manner and detail they report such flow cytometry results to clinicians. Flow cytometry immunophenotyping may be ordered when you have an increased number of lymphocytes or sometimes an increase in another type of white blood cell WBC anemia a decreased platelet count or immature WBCs that are not normally seen in the blood.
FC may also have a place in the initial diagnostic investigation of aggressive lymphoma. FLOWLL Back To Search ORDERING SPECIMEN PROCESSING RESULTS For outreach patients only. The survey indicated that a large number of markers are routinely evaluated to phenotype leukemias mean 19 and lymphomas mean 16.
Gelain Remove constraint gelain Subject flow cytometry Remove constraint Subject. When using fresh tissue for flow cytometric immunophenotyping the predominant populations are lymphoid. Testing begins with decisions about which screen test panels to use for individual samples as they are received by the laboratory.
Disease Overview DiagnosisTreatment Issues. Flow adds to the confidence of the reporting by specialist pathologists of type of lymphoma. These can be stratified as large and small lymphocytes CD45 positive.
The advantages of flow cytometry are based largely on its ability to analyse rapidly and simultaneously multiple cell properties in a quantitative manner. Flow cytometry may be used to characterize and count types of white blood cells in the evaluation of infectious diseases autoimmune disorders or immunodeficiencies. However bcl-2 can be expressed in 10 to 20 of cases.
Phenotypic assessment of lymphoid cells can be done with flow cytometry. CD10 CD38 CD43 CD71 and bcl-6 are also expressed. The tumor cells are negative for CD5 CD23 and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase TdT and usually negative for bcl-2.
However flow cytometry results usually make certain lymphoma entities extremely likely and others very unlikely. Light scatter gating using CD4514 to monitor the gate selected is currently employed by a 2l ratio. SHC and LPCH patients order PATH22 blood PATH23 bone marrow or PATH24 specimen type other than blood or bone marrow.
Additional cell surface cytoplasmic or nuclear marker each 88187-Flow Cytometry Interpretation 2 to 8 Markers if appropriate 88188-Flow Cytometry Interpretation 9 to 15 Markers if appropriate. Toggle facets Limit your search Text Availability. Flow Cytometry to help determine the exact type of lymphoma or exclude lymphoma This test also looks for certain molecules on the outside surface of cells by which antibodies protein molecules stick helping to identify what types of cells they are.
In general FCM has been found to be more sensitive compared with cytomorphology 6 7 13 14. Thakhi et al demonstrated that in non-hodgkins lymphoma flow cytometry has greater sensitivity reduced interpretive subjectivity and faster turn-around time compared to immunohistochemistry. Due to the results of the pilot study we now routinely use flow cytometry for all our lymph node samples for possible lymphoma.
Flow Cytometry For LeukemiaLymphoma Diagnosis ORDER CODE. Manner and detail they report such flow cytometry results to clinicians. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping is useful in diagnosing lymphoma under the WHO classification system where lymphoid neoplasms are separated into distinct clinical entities based upon morphology.
Veterinary immunology and immunopathology 5. The gating dot plot below identifies a predominant CD45 bright FS small used cells. Flow cytometry to be discussed in detail in another Morning Report is a powerful technique that allows for phenotyping of unfixed cells in fluid.
First cell surface cytoplasmic or nuclear marker x 1. Flow cytometry FC is usually recommended for the classification and staging of lymphomas in patients with organomegaly and atypical cells in effusions and blood after the exclusion of other possible diagnoses. Quick turn around time for flow cytometry of 24-48 hours which speeds diagnosis especially of high grade disease.
Lineage identification can provide a confirmatory diagnosis or differential diagnosis prognosis and treatment options. Citation in PubAg 15.
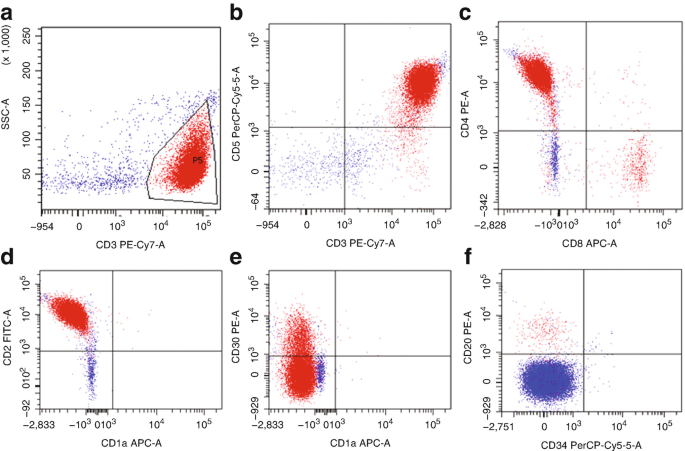
Flow Cytometry Of Mature And Immature T Cell Lymphoma Springerlink

Flow Cytometry Analysis Of Mice Splenocytes For The Three Download Scientific Diagram

Flow Cytometry Gating Logic For Detection Of Activated Platelets Download Scientific Diagram

Flow Cytometry Analysis Of Lymphocyte Gated Bone Marrow And Spleen Download Scientific Diagram

Flow Cytometry Of The Bone Marrow And Peripheral Blood Of Patient 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Impact Of Flt3 Receptor Cd135 Detection By Flow Cytometry On Clinical Outcome Of Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma And Leukemia

Flow Cytometric Dot Plots Showing Patterns Of Sig Lcs Negative A B Download Scientific Diagram

Cd45 Vs Side Scatter In Clinical Sample Gating A In Clinical Flow Download Scientific Diagram

Selected Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping Plots From Fine Needle Download Scientific Diagram

Diagnostic Flow Cytometry In Cytology Springerlink

Flow Cytometric Presentation Of A Large B Cell Lymphoma A Forward Download Scientific Diagram
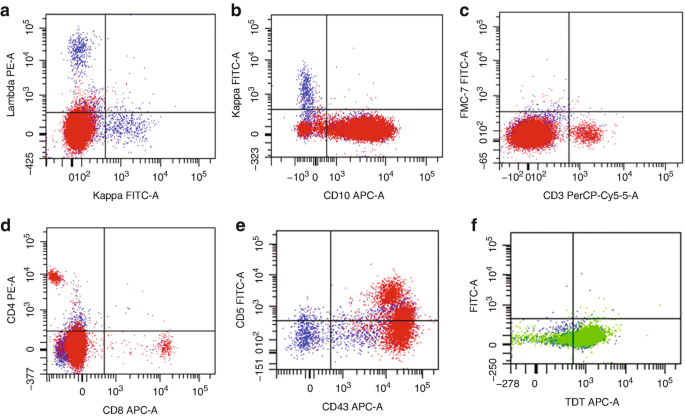
Flow Cytometry Of Mature And Immature T Cell Lymphoma Springerlink

Flow Cytometric Analysis Of Pb Derived Leukocytes Cd45 And Lineage Download Scientific Diagram
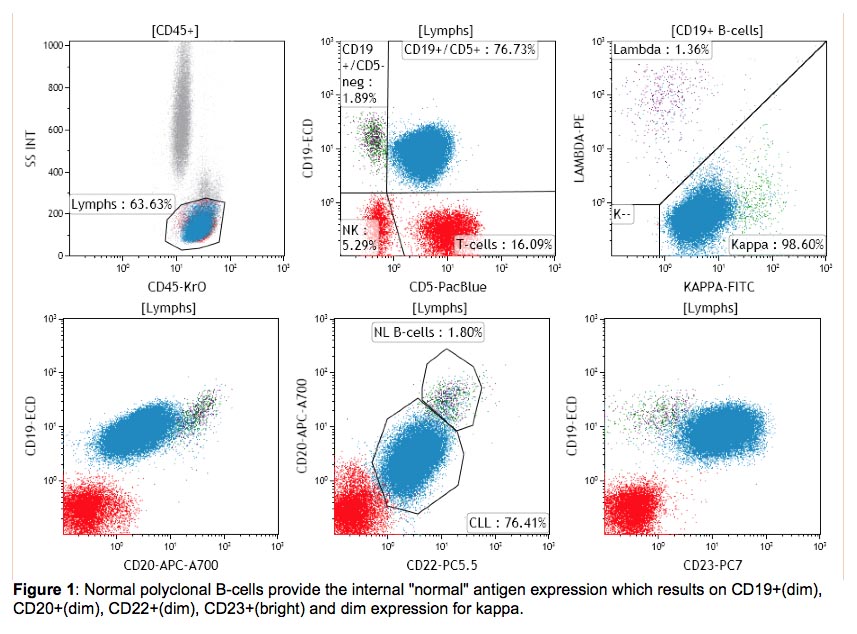
International Clinical Cytometry Society

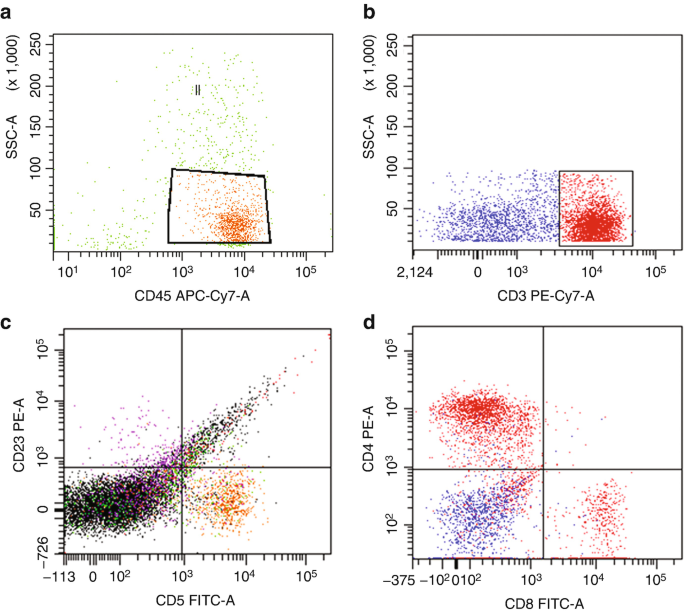
Flow Cytometry Of Mature And Immature T Cell Lymphoma Springerlink

Flow Cytometry Demonstrating Cd10 Expression On Mycosis Download Scientific Diagram

Flow Cytometry Demonstrating Cd10 Expression On Mycosis Download Scientific Diagram

Flow Cytometry Results Flow Cytometric Graphs Showing Positivity For Download Scientific Diagram
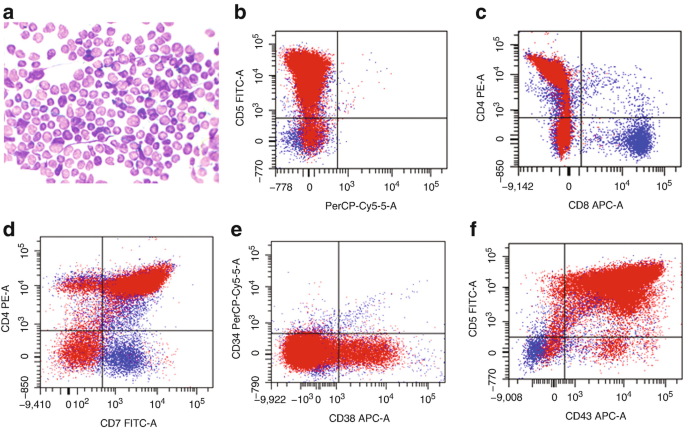
Flow Cytometry Of Mature And Immature T Cell Lymphoma Springerlink